Ditch the book’s meaningless reading and embrace these Effective Study Techniques for easy A+ grades.
While there’s no single approach that guarantees success, there are effective study techniques that can help you focus, stay engaged, and maximize your learning. Simply reading from textbooks and hoping to grasp complex concepts is often insufficient. Many students rely on ineffective study habits that hinder their academic progress.
This blog post is specifically designed for students like you, and it delves into 7 essential study techniques that every student should master before embarking on exam preparation. These techniques will equip you with the skills and strategies to unlock your full potential and achieve A+ grades with ease.
Pomodoro Technique
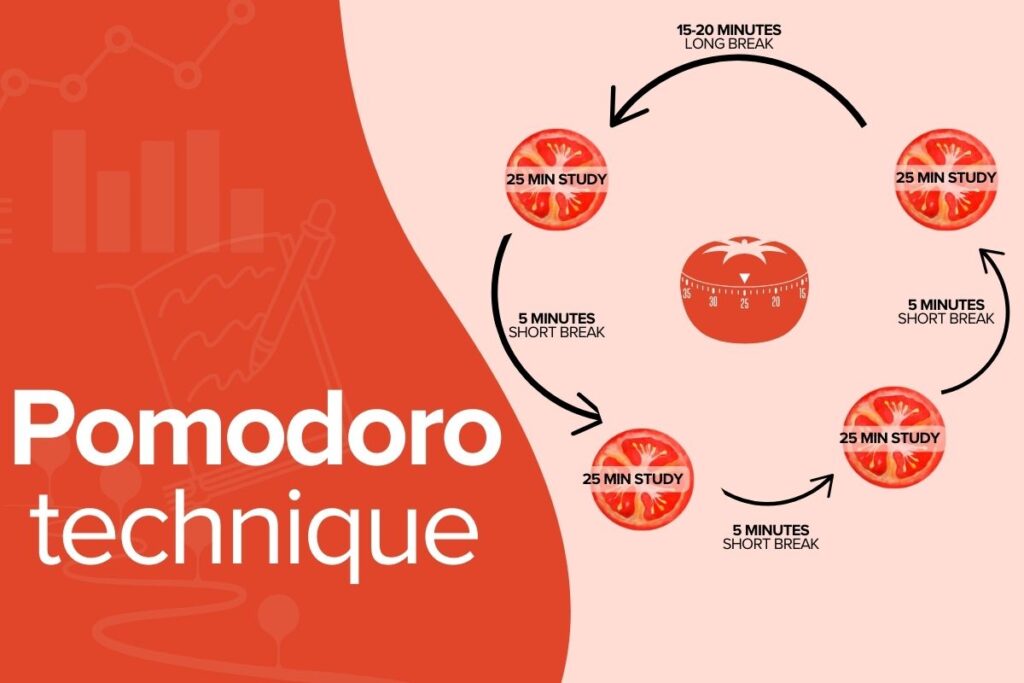
The Pomodoro Technique, or the 25-minute study method, is one of the most popular study techniques that focuses on time management and effective methods to study anything while deeply focusing on the subject. This study technique is especially popular because it is useful to keep your learning process on track, without getting distracted from the main goal.
How does the Pomodoro Technique work?
The first step is choosing the topic or lesson you want to study during a session. After choosing that topic, set a timer for 25 minutes, get to work, and don’t get distracted. Phones are not allowed. When the buzzer sounds, take a 5-minute maximum study break. When the break finishes, set the timer again for 25 minutes. Then repeat for four sessions. Keep a list of topics or lessons that you want to go through before the exam. Strike through the lesson you have just finished.
Why it works?
Usually, a 25-minute studying session is enough to not lose your focus and not feel like a chore. You get little work done that doesn’t burden you while setting you on track for learning a full topic within the four Pomodoro sessions. If you feel that a 25-minute session is not enough, you can increase it to a 30-minute session with a 5-minute break.
The Pomodoro Technique is useful, especially for those who have a hard time focusing on studying or for those who feel that the topic is extensive and hard to learn. Even though it’s widely popular, it remains one of the best study methods with breaks you can put into practice for a straight A+ on all your exams.
The Feynman Technique

Richard Feynman was an American physicist who made significant contributions in difficult areas such as quantum mechanics and particle physics, which eventually led to his earning a Nobel Prize in 1965. Despite his hard work being recognized with the prestigious Nobel Prize, Richard Feynman never considered himself as anything more than a regular person who simply studied hard, a mindset that eventually led to him winning this distinguished prize.
There’s no miracle people. It just happens they got interested in this thing and they learned all this stuff. There’s just people.
Richard Feynman
What is the Feynman Technique?
The Feynman Technique is a four-step process for internalizing and assimilating any topic. It is such an effective study technique because it replaces memorization by heart with learning a certain topic in depth.
The four steps of the Feynman Technique are:
- Choose a topic to learn: select a topic you must learn or you are just purely interested in and write it as a title at the top of the page in a notebook (or Google Docs if you prefer)
- Teach it to yourself as you would to a toddler: start writing your knowledge about the subject in your notebook as you would explain it to a toddler. This step is particularly important when learning a difficult subject before an exam because it makes sure you 100% understand the concepts behind the topic.
- Identify gaps and areas to improve: identify gaps in your understanding of the subject. Be sincere with yourself and try to revise any areas you wish to improve and learn more about when using this technique. Use “why” questions.
- Organize and simplify: Organize your notes in a way that makes sense to you. It should look like a story you can easily tell to anyone and they will understand as well, even though they lack knowledge on the subject.
Simply knowing the name of something, doesn’t mean you understand it. The Feynman Technique nurtures a process of growth by starting to learn like a child once again.
Distributed Practice
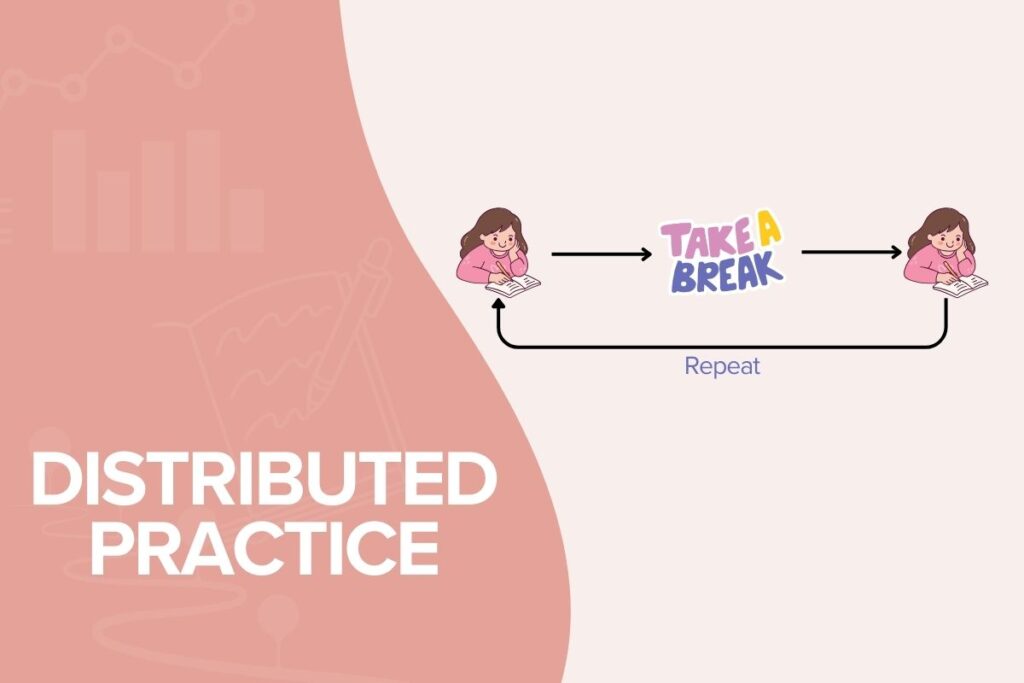
Distributing study sessions over time, rather than cramming everything in one go, is known as distributed practice. Studies have shown that distributed practice results in better long-term retention, even when the total study time is equal. This advantage is attributed to the spacing effect, which suggests that spaced reviews of the same information are more effective for long-term memory consolidation.
Why is it an amazing study technique?
Distributed practice is an amazing study technique because it effectively enhances the long-term retention of information. By spacing out study sessions and incorporating retrieval practice, distributed practice mimics the way our brains naturally consolidate memories, leading to deeper understanding and improved recall.
Like a well-structured workout, distributed practice provides intermittent breaks, that allow your brain to rest, consolidate information, internalize it, and recharge for future study sessions. If you wonder how to learn math or a new language, the answer lies in systemizing the information and learning vocabulary words or equations over multiple study sessions before taking an exam or a test.
In contrast, by cramming all of your studying into one long and difficult session, your brain will be overloaded with information, which will eventually lead to inefficient retention, a higher likelihood of forgetting, and a tired, demoralized brain. On the other hand, distributed practice allows your brain to gradually and effectively absorb information and transform it from short-term to long-term memory.
Therefore, distributed practice stands out as an efficient study technique that promotes deeper understanding, improved retention, and long-term learning success. It’s like giving your brain the time and space it needs to build a stronger foundation for knowledge, making it a worthwhile investment in your academic grades.
Try Goodnotes for flexible note-taking.
Mind Map
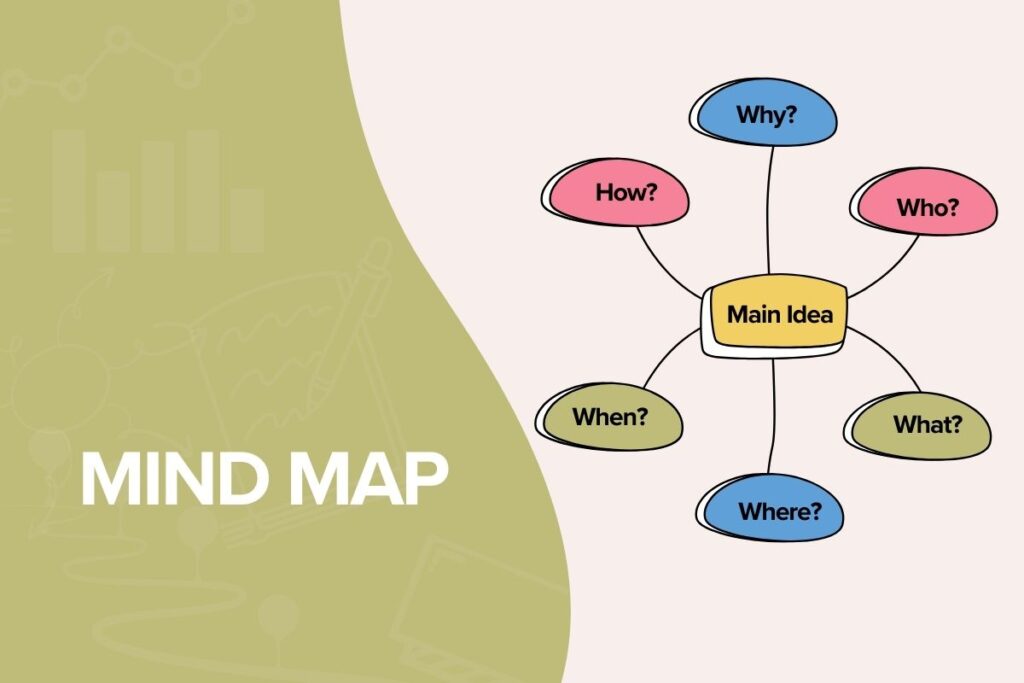
The Mind Map Technique is a powerful tool for visual thinking, brainstorming, and memory enhancement. It helps you to see the big picture, identify connections between ideas, and remember information more effectively. Mind mapping is also a great way to generate new ideas and solve problems.
How to make a mind map for studying?
It is relatively easy to create a mind map that works and will get you a straight A on your exam or test. Why? Because it improves memory, helping you encode information and making it easier to remember, helps you enhance your creativity, and pushes you to think outside the box. Moreover, it can help you stay productive, organize your thoughts and tasks, and improve problem-solving,
If you are a visual learner, follow the steps below to create your mind map.
First Step: Grab a piece of paper and rotate it horizontally.
Second Step: Draw key branches from the central topic and color-code them for better comprehension.
Third Step: Draw sub-branches if you think this may help you with your learning process. Ask yourself the 6 key questions for a successful mind map: Why? What? When? Where? Who? How?
Use this platform if you want to create your digital Mind Map: Simple Mind and Miro.
Useful study tools
Convert PDF to PowerPoint: Upload your PDF and convert it to a fully editable PowerPoint in a matter of seconds.
Matchcha: Write math equations easily online
Evernote: great note-taking, project planning software
Effective learning should be effortless, engaging, and productive. The Mind Map study method embodies these advantages, transforming studying into an enjoyable experience. Visual learners use this study technique for exams due to grasping concepts thoroughly and active learning.
Spaced Repetition
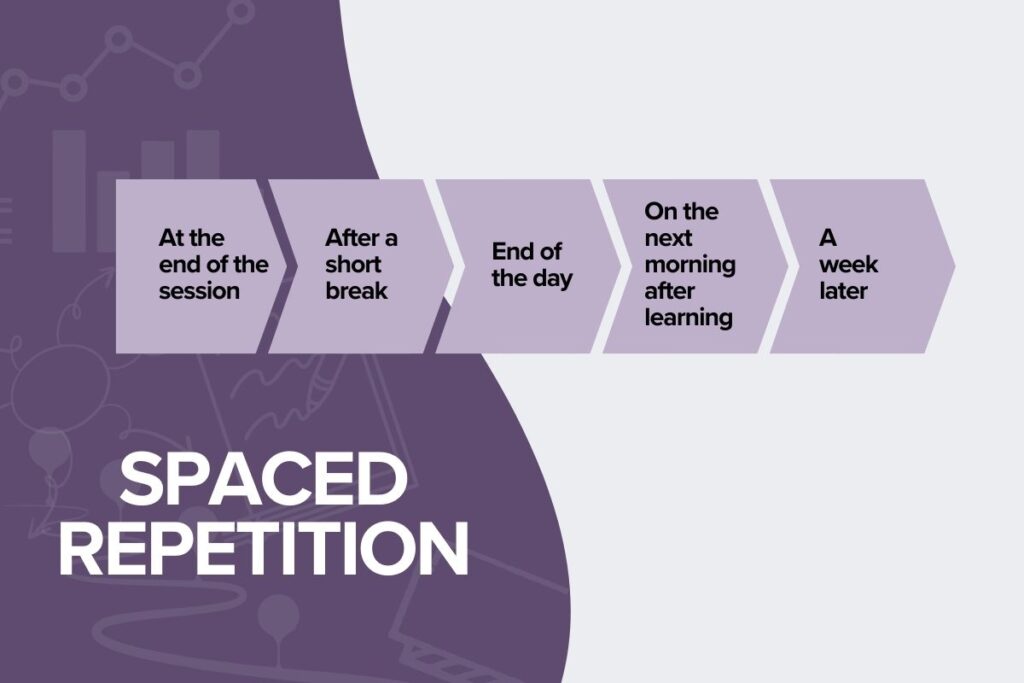
Spaced repetition, one of the distributed practice methods, is a highly effective study technique that encourages students to spread out their study sessions over time instead of studying everything the night before an exam. This technique relies on the natural process of memory consolidation, which occurs when our brains strengthen neural connections between learned information. When we revisit and review material at spaced intervals, we force our brains to work harder to retrieve the information, which strengthens the underlying neural pathways and makes it easier to retain the information over the long term.
Here’s a simple schedule to follow when using spaced practice:
Day 1: Learn the material in class.
Days 2-3: Revisit and review the material.
Week 1: Revisit and review the material.
Week 2: Revisit and review the material.
By following this schedule, you’ll be providing your brain with ample opportunities to consolidate the information, leading to improved comprehension, retention, and recall for your exams.
To make the most of spaced practice, it’s crucial to start early and plan your study sessions accordingly. From the beginning of a semester, schedule dedicated time each day to review and revisit the material. This proactive approach will not only help you retain the information more effectively but also prevent last-minute cramming.
Remember, spaced repetition is an adaptable technique that can be applied to various learning goals and subjects. Whether you’re preparing for a biology exam, seeking to enhance your math skills, or tackling a new language, spaced repetition can equip you with effective study techniques that will enhance your learning process and boost your exam performance.
Cornell Note-Taking
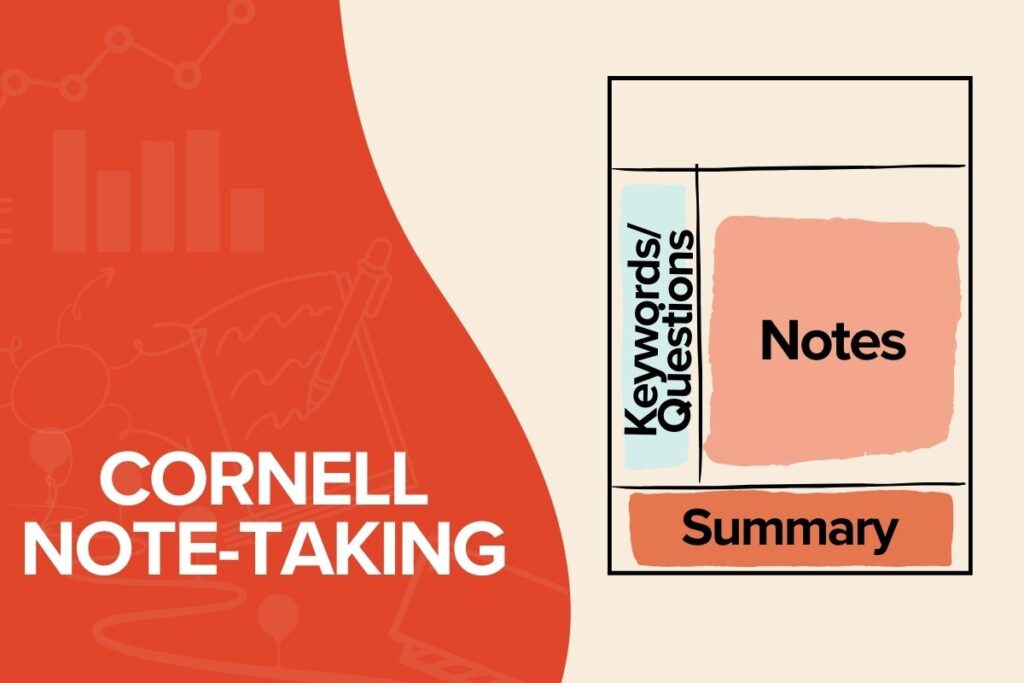
If you are a student having a hard time coming up with a personalized system to take notes, the Cornell Note-Taking method is the one that will ensure you will easily structure your lecture, making the most out of your time when you revise it.
There are many ways to take notes. However, research shows that taking notes by hand is more effective than digital ones. The act of writing can aid you in remembering better than just listening to your teacher or reading from PowerPoint slides or books.
How to take notes effectively in class?
Start by labeling your page and divide it into three sections:
A Note-Taking Area: Add most of your lecture’s content there.
A Keyword & Questions Area: When taking notes, add keywords and/or questions you didn’t fully understand. Revise and reflect on them after the lecture.
A Summary Section: Summarize what you’ve learned.
Aside from its efficiency in note-taking, the Cornell note-taking method offers another advantage: rapid information absorption, which promotes effective learning. Due to the overview provided, the lecture material can be easily revisited, allowing for a quicker grasp of the core concepts. This study technique is particularly beneficial for students who want to enhance their learning and retention abilities.
Leitner System
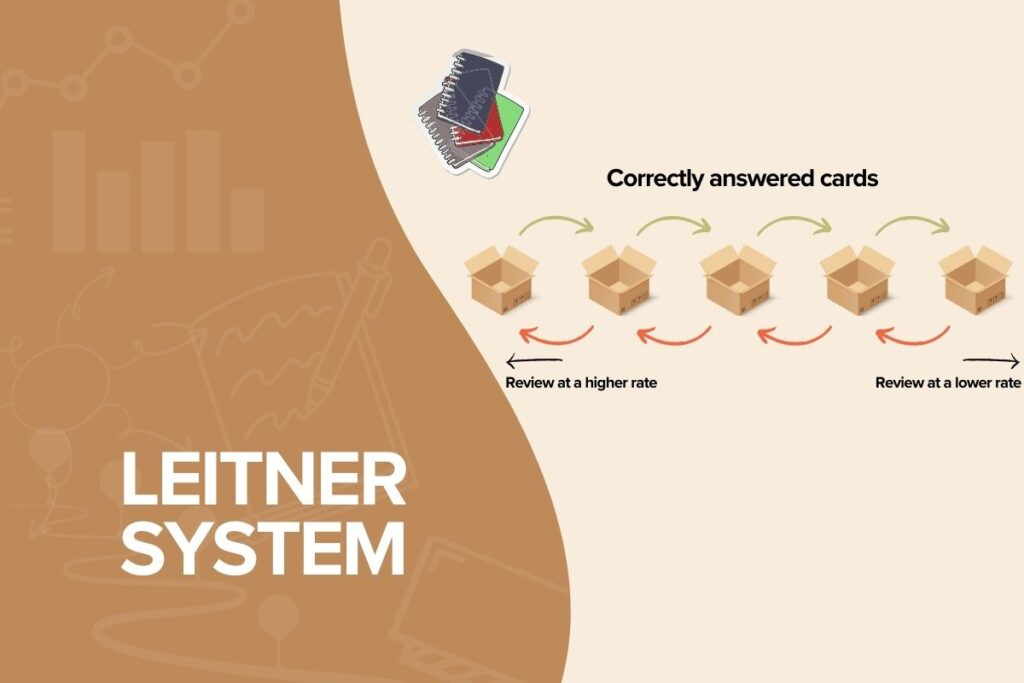
If you are the type of person who loves to use flashcards when studying, the Leitner System for Flashcards is the best study method for you. The Leitner System is a learning method that emerged from the Distributed Practice family of study techniques. This system involves grouping cards according to how well you remember their content and practice learning them with a different frequency. One of the main advantages of this method is that it helps you revise more frequently the cards you may have a hard time remembering than those that are easy to learn.
The Basic Principles of the Leitner System
Organize your flashcards into different folders based on their level of difficulty: easy, medium, and difficult. Prioritize reviewing the flashcards in the medium and difficult folders more frequently to ensure they are firmly remembered by your memory. This approach ensures that you consistently focus on the most difficult concepts until they are mastered.
Unlike traditional cramming methods, the Leitner System prioritizes reviewing challenging concepts more frequently, allowing for a deeper understanding and longer-lasting information retention. This efficient approach minimizes time spent on well-understood material, focusing instead on areas that require more attention.
Conclusion
Implement these effective study techniques to transform your learning experience and achieve academic excellence. Remember, studying is not passive; it requires proactivity, critical thinking, and a willingness to apply your knowledge.
Don’t forget to pair these effective study techniques with my 37 habits that will make you a smarter person list and my top 5 tips to increase productivity. Also, learn more about the Eisenhower Matrix and time management.






Pingback: How to Empower Your Students to Become Independent Learners: 5 Methods
Pingback: 7 Ways to Build Self-Discipline That Lasts Forever